Advantages of Embryo Freezing
Embryo freezing offers several advantages in the context of assisted reproductive technology, particularly in in vitro fertilization (IVF):
- Maximizing Chances of Pregnancy: Since only a limited number of embryos can be transferred during a single IVF cycle, remaining quality embryos can be frozen for future use. If the initial transfer does not result in pregnancy, couples have the option to transfer frozen embryos without undergoing new ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval, reducing emotional and financial stress while increasing the chances of pregnancy.
- Facilitating Future Pregnancies: If a couple successfully achieves a live birth, frozen embryos can be used for subsequent pregnancies without the need for additional hormone treatments, making family planning more manageable.
- Dealing with Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): In cases like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), where excessive egg production can lead to hormonal imbalances, freezing all embryos allows for postponing embryo transfer to a later cycle, thereby minimizing risks associated with OHSS.
- Addressing Endometrial Issues: If an expectant mother experiences issues such as insufficient endometrial thickness, the presence of endometrial polyps, or breakthrough bleeding during the IVF process, freezing embryos allows for treatment of these issues before proceeding with the transfer.
How Are Embryos Frozen?
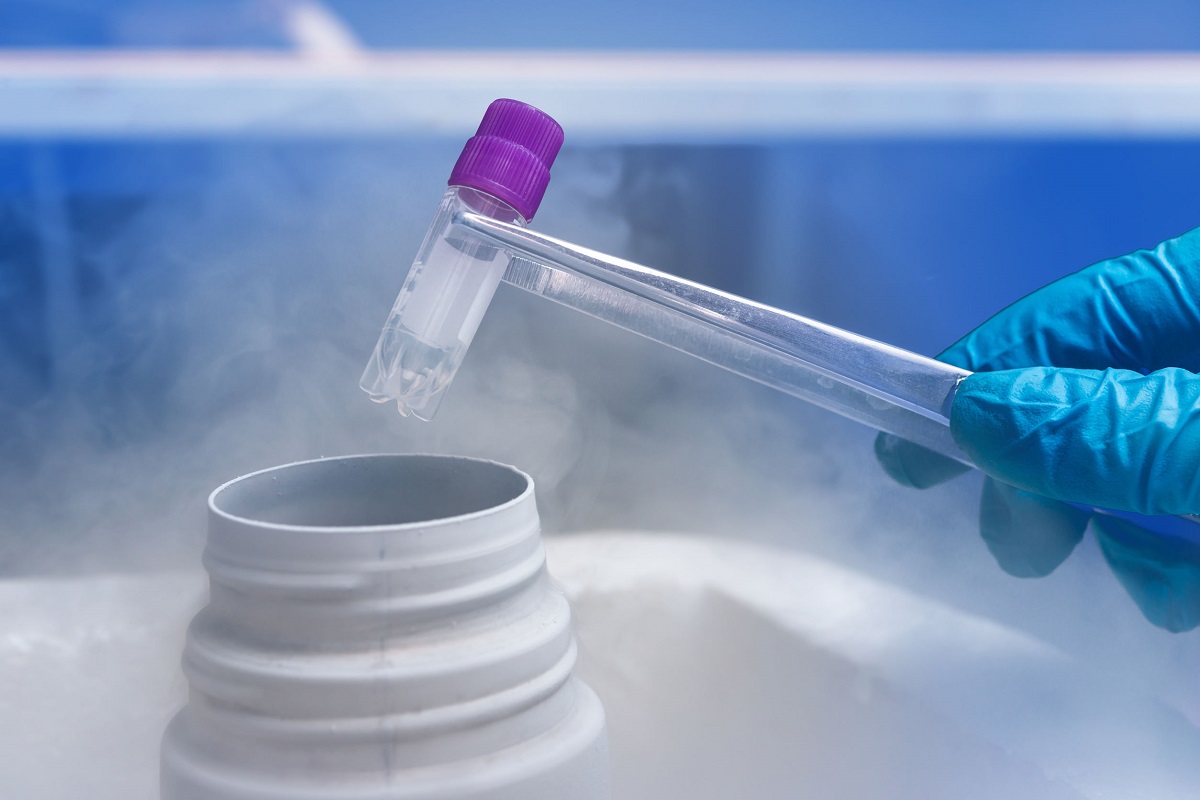
Embryos can be frozen at various developmental stages using advanced technological methods. They undergo specific procedures in a protective solution before being placed in specialized containers. After this preparation, embryos are frozen in liquid nitrogen at -196 degrees Celsius and stored in designated compartments for each patient.
Duration of Storage for Frozen Embryos
The duration for which embryos can be stored varies by country. In Turkey, the standard storage period for frozen embryos is five years, and extensions require permission from the relevant authorities.
Viability and Pregnancy Rates After Thawing
The survival rate of thawed embryos can be as high as 95%. In practical terms, this means that out of every ten frozen embryos, approximately nine have a chance of leading to pregnancy. However, laboratory conditions during the embryo culture phase can sometimes impact success rates. If thawed embryos develop well in suitable conditions, the pregnancy rates can be comparable to, or even higher than, fresh embryo transfers.
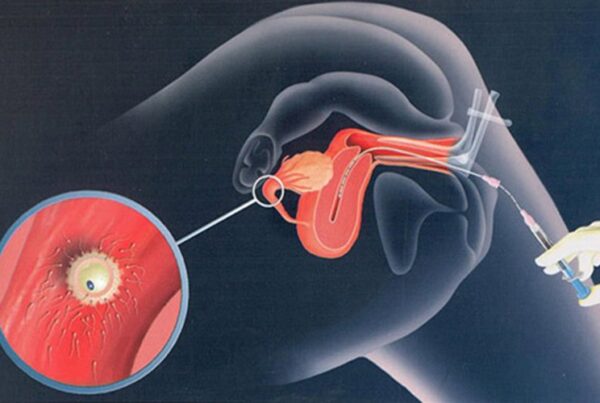
How Are Thawed Embryos Transferred?
To prepare for the embryo transfer, the endometrium (the uterine lining) must be adequately prepared and reach sufficient thickness. This preparation often involves hormonal treatments to optimize conditions for embryo implantation. Once the endometrial lining is ready, thawed embryos can be transferred into the uterus.